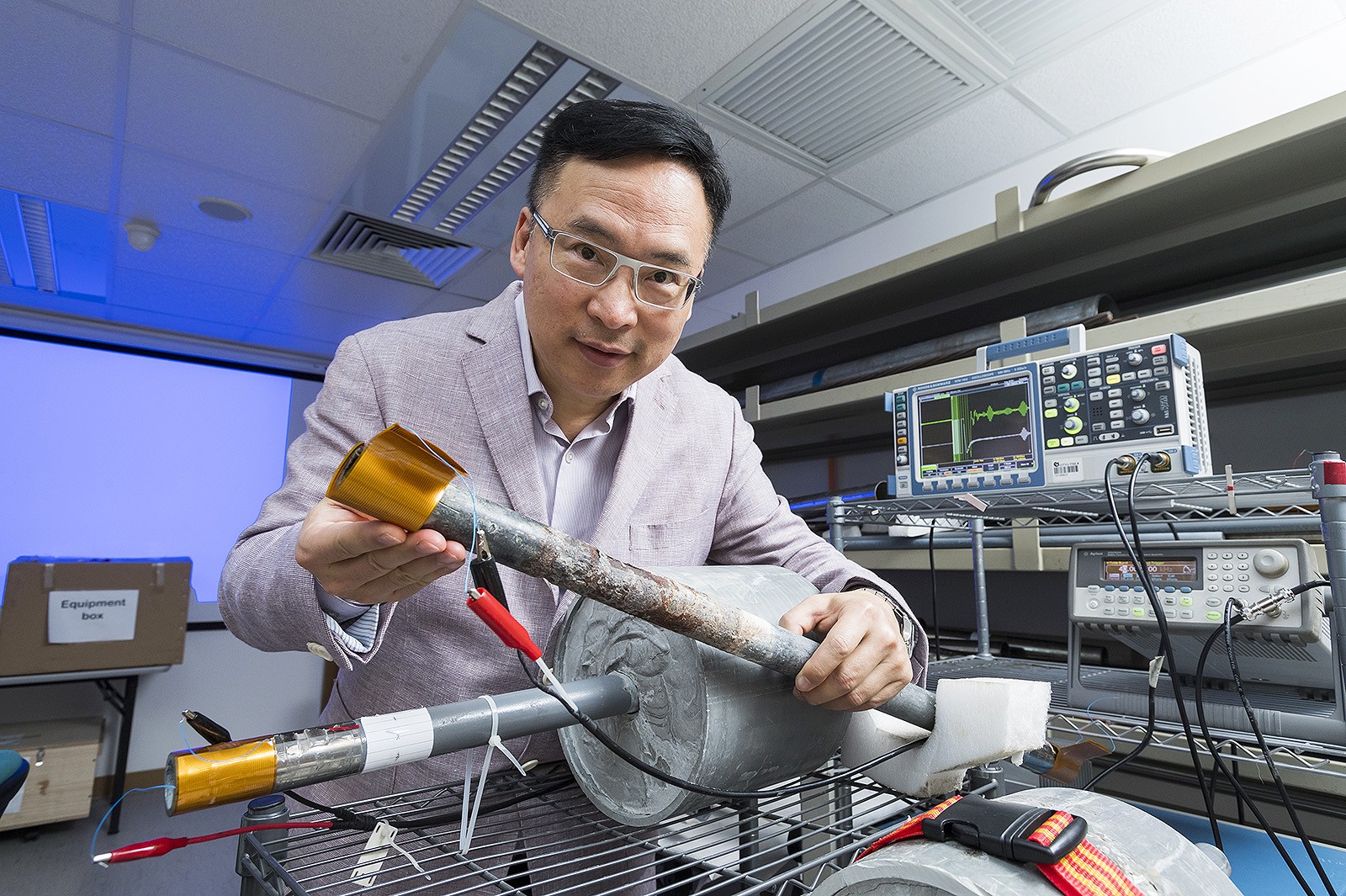
A research team from the Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management (SEEM) at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed the world’s first non-destructive-testing based inspection system that can detect corrosion in buried and wall-covered pipes.
The system, which detects wall-covered corrosion within an inaccuracy rate of less than 2.1%, combines ultrasonic guided wave (GW) technology with an innovative GW sensor designed by the CityU team as well as cutting-edge signal processing methods.
Experiments show that the system can accurately inspect the condition of a pipe that’s over 70 metres long, which has the potential for detecting the length of reinforcing steel bars buried in concrete and cracks in railway tracks.
This non-destructive-testing based inspection system is superior to the current ultrasonic testing method, according to the lead investigator of the project, Dr Peter Tse Wai-tat, Associate Professor at SEEM and the Director of the Smart Engineering Asset Management Laboratory.
“GW technology makes long-range and thorough inspections possible by using a single transducer that’s more effective and accurate than the traditional ultrasonic testing method,” he said.
Pipes buried underground and in concrete walls are prone to corrosion under humid condition. Severe corrosion can lead to pipe ruptures and water or gas leaks. The latter can pose a serious threat. The new inspection system locates defects in buried pipes and detects the extent of any corrosion. This means pipes can be replaced earlier and helps to reduce risks and costs.
Dr Tse said the system used a novel sensor made of smart materials and flexible induction-coils. It makes use of the magnetostrictive effect to generate GW in the pipes. Even if the inspected pipes have multiple coatings and are buried in concrete walls, the system can still detect the extent of corrosion.
The system is easy to use. First, install the self-developed software in a portable computer. Then connect a USB-based data acquisition box and a novel sensor. This sensor is designed as a few thin sheets and can easily wrap around exposed parts of the pipe. After the connections are made, the system can generate particular GW signals and receive signals reflected from the pipe in less than one second. If the pipe has many bends and joints, the number of inspection points has to be increased.
Both laboratory experiments and field tests, the latter inspecting in-service building pipes with the help of The Hong Kong and China Gas Company Limited (Towngas), have proved that the GW system is effective at detecting corrosion.
The research project was funded by the Innovation and Technology Fund and Towngas. CityU plans to enter into a licensing agreement with MSDI Group to commercialise this research and development achievement.