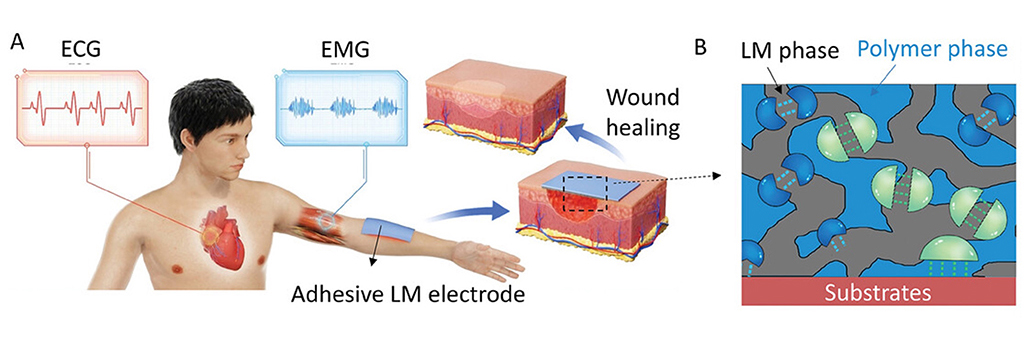
Liquid metal (LM) bioelectronics has a wide range of applications in medical devices and medical implants. However, current LM-based electrodes have difficulties in achieving a combination of properties, including stable conductivity, high tissue adhesion, stability, good biocompatibility, degradability, and recyclability. In view of this, a multidisciplinary research team consisting of members from Prof. Xi Yao and Prof. Mingliang He’s groups from City University of Hong Kong has prepared a stable LM electrode with extremely high adhesion strength (8.9 MPa), which can be further adjusted in a wide range. The adjustable adhesion strength can greatly expand the material’s application scenarios. For example, high adhesion strength ensures a stable electrical connection to the integration of rigid electronic components, while low adhesion strength makes it comfortable to contact with wound skin, which can facilitate the management of skin wound and the application of epidermal devices. Taking advantage of its tunable surface adhesion and biocompatibility, the prepared LM electrode provides a more reliable and friendly method for the development of epidermal devices for healthcare management. This research was recently published in Advanced Functional Materials, with Prof. Yao and Prof. He as corresponding authors. The lead first author is Dr Chunyan Cao, a PhD graduate from Prof. Yao’s group and now an associate professor at Nantong University. The other co-first authors are Dr Changshun Hou and Dr Xiong Wang.